Beim Laden der Seite ist ein Fehler aufgetreten.
Bitte aktualisieren Sie den Browser und versuchen Sie es erneut. Wenn das Problem weiterhin besteht, kontaktieren Sie uns bitte.
EliteSiC Solutions for Energy Storage Systems

Overview
Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) is a fast-growing industrial market to meet the power storage demands of the switch from carbon-based energy sources to more renewable and sustainable methods. Many countries also offer incentives to install these energy storage systems, which has increased the need for energy storage in residential, industrial, and commercial applications. Energy storage systems are needed in Solar Systems and EV Charging Stations, using similar components and topologies as well.
System Implementation
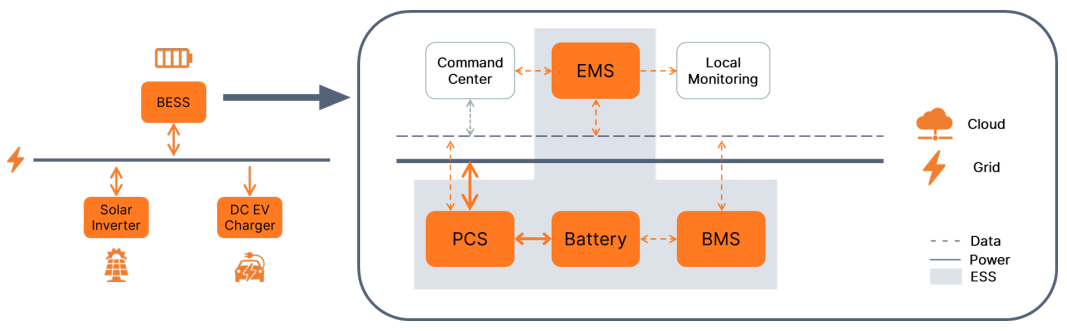
System Description
Four Elements to Build BESS
A BESS is made up of 4 parts, whether it is for residential or commercial use. Battery packs consist of hundreds or thousands of battery cells to set up a commercial level system, and high-voltage modules are integrated into the battery racks or banks for higher capacity. Charging and discharging voltages typically range from 50 V to 1100 V, dependent on the battery voltage and circuit topology. BMS (Battery Management System) is an electronic system managing rechargeable batteries by ensuring batteries are operating in SOA (Safe Operating Area), monitoring operating states, calculating and reporting real-time data, etc. to ensure a longer operational life. PCS is another important sub-system for bidirectional conversion of energy between the battery pack and the grid and/or load, a big factor in determining the system cost, size and performance. EMS is a software-based system of computer-aided tools used by operators of electric utility grids to monitor, control, and optimize the performance of the generation or transmission system.
AC-coupled System and DC-coupled System
BESS is currently segmented into 2 types, AC-coupled and DC-coupled systems. AC-coupled BESS is a separated system that can be added to existing solar/energy generation system/grid, making it an easy upgrade. However, it requires additional power conversion stages to accomplish full charging/discharging, leading to higher losses. On the other hand, DC-coupled system, commonly employed in residential hybrid solar inverters, offer extra energy storage capacity by connecting to the DC bus. It involves single DC-DC conversion step but requires a decision during product design, as DC bus voltage is often high and may pose safety or retrofitting challenges.
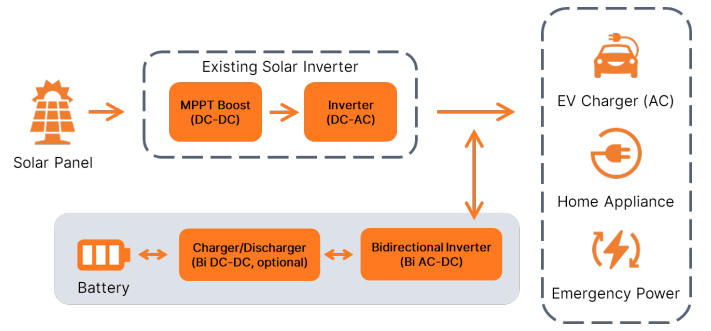
Figure 2: AC-coupled System
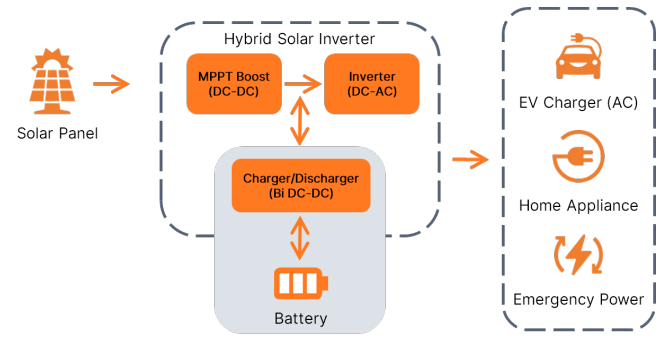
Figure 3: DC-coupled System
Bidirectional Operation
The power conversion stage of BESS requires bidirectional operation. Commonly, three-phase inverters can be bidirectional and behave as an AC-DC converter when operating in reverse mode, reactive mode for UPS or braking mode for motor drive. In general, power converters, and in particular topologies, are optimized for one use case and one direction of the power flow through the selection and relative sizing of the switches and diodes. Three−phase inverters used as AC-DC converters in PFC mode will not be as efficient as an optimized AC-DC PFC converter. Even DC-AC topologies designed to be bidirectional will show better performance in one direction than the other. So, it is important to bear in mind what will be the most common use case. Also, bidirectionality will not be achievable with all topologies, so selecting the right one upfront is an important factor. Read AND90142 - Demystifying Three-Phase Power Factor Correction Topologies to understand three-level technology and featured three-level PFC circuits.
Use Silicon Carbide Products in PCS
Compared to IGBT, Silicon Carbide (SiC) devices have more advantages in high-voltage and high-current applications, such as enabling high-frequency switching. Although IGBT remains the preferred choice in BESS design, considering different switching strategies, incorporating SiC devices in certain sections can yield superior performance. For instance, in the bidirectional inverter using A-NPC, SiC devices may be selected in the inner legs to reduce switching losses because of the dedicated switching strategy requiring high switching frequency of inner switches, while the rest switches can still utilize low VCE(SAT) IGBTs to maintain controllable cost.
Learn more about Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) by downloading the onsemi BESS System Solution Guide here!

Additional Links
Specifications
Data Sheet
Reference Designs
EliteSiC Discretes
Highly Optimized EliteSiC Discretes
Leveraging onsemi’s leading position, technologies and expertise in MOSFETs and IGBTs, EliteSiC Discretes are optimized for performance requirements of vehicle electrification and energy infrastructure applications. These optimizations include improved switching losses, robustness and The breadth of packaging portfolio from standard to application specific packages.
With a deep application expertise in EV (on-board and off-board), industrial, and system-level simulation tools, you count on onsemi to deliver innovative solutions that provide you a competitive edge.
PLECS-based system-level simulation tools (Elite Power Simulator & Self-service PLECES Model Generator) will enables faster and more accurate prototyping for design simulation, helping achieve a faster time to market. System-level simulations of complex power electronic applications are critical for first-time-right design. onsemi's Self-Service PLECS Model Generator enables engineers to create custom high-fidelity PLECS models. Use them in your simulation platform or upload to Elite Power Simulator for seamless simulation.
| SiCMOSFETs | SiCDiodes | |
| 650V | Link to all 650V SiCMOSFETs | Link to all 650V SiCDiodes |
| 900V | Link to all 900V SiCMOSFETs | |
| 1200V | Link to all 1200V SiCMOSFETs | Link to all 1200V SiCDiodes |
| 1700V | Link to all 1700V SiCMOSFETs | Link to all 1700V SiCDiodes |
Specifications
Data Sheet
Reference Designs
EliteSiC Modules
SiC & SiC/Si Hybrid Modules for EV Charging
onsemi offers the most comprehensive portfolio of PIMs to address the key topologies on the market. This gives designers the flexibility to pick the right PIM for power conversion stages in their DC fast charging or energy storage system applications. To accelerate the design cycle, advanced piecewise linear electrical circuit simulation (PLECS) models through our Self-Service PLECS model Generator and application simulation with the Elite Power Simulator of this portfolio will also be made available to designers.
For each module, onsemi uses die from the same wafer to ensure more consistency and reliability so designers don’t have to use discretes from different suppliers, which can lead to varying performance results. In addition to its reliability, this module portfolio offers the following benefits:
- • Uses the Gen3 M3S SiC MOSFET technology which offers the lowest switching losses and highest efficiency in the industry
- • Supports key topologies such as multi-level T-type neutral point clamp (TNPC), half-bridge and full-bridge topologies
- • Supports scalable output power from 25 kW to 100 kW, enabling multiple DC fast charging and energy storage systems platforms including bidirectional charging
- • Industry-standard F1 and F2 packages with the option of pre-applied Thermal Interface Material (TIM) and press fit pins
- • Enables optimal thermal management, avoiding system failure due to overheating
- • Full SiC modules offer energy conservation by minimizing power losses, directly translating to cost and energy savings
- • Offers more robustness and dependability, ensuring consistent operations
Specifications
Data Sheet
Reference Designs
IGBTs
IGBTs for EV Charging
Field Stop VII, IGBT, 1200 V
- • New Family of 1200 V Trench Field Stop VII IGBT
- • Trench narrow mesa & Proton implant multiple buffer
- • Fast switching type and low VCE(SAT) type available
- • Improved parasitic cap for high-frequency operation
- • Common packages
- • Target applications - Energy infrastructure, Factory Automation
Specifications
Data Sheet
Reference Designs
Gate Drivers
Pairing Gate Drive to EliteSiC
“Energy Infrastructure applications like EV charging, energy storage, Uninterruptible Power Systems (UPS), and solar are pushing system power levels to hundreds of kilowatts and even megawatts. These high-power applications employ half bridge, full bridge, and 3-phase topologies duty cycling up to six switches for inverters and BLDC. Depending on the power level and switching speeds, system designers look to various switch technologies, including silicon, IGBTs, and SiC, to best fit application requirements.
While IGBTs offer superior thermal performance vs. silicon solutions in these high-power applications, EliteSiC by onsemi enables both higher switching speeds and high power. onsemi offers a complete portfolio of SiC MOSFETs ranging from 650V to 1700V breakdown voltage, with RDSONs as low as 12mΩ. But, every SiC MOSFET requires the correct Gate Driver to maximize system efficiencies and minimize the total power losses. This easy-to-use table below pairs the correct Gate Driver to each SiC MOSFET”.
| EliteSiC MOSFETs | Gate Driver: 5kVRMS Galvanic Isolation | ||||||
| GI: 3.75kVRMS | GI: 5kVRMS | ||||||
| 1-Channel (source/sink) | 2-Channel (source/sink/matching) | ||||||
| V(BR)DSS: | RDSON (typ): | Package: | 4.5A / 9A | 6.5A / 6.5A | 7A / 7A | 6.5A / 6.5A / 20ns | 4.5A / 9A / 5ns |
| 650V | 12 – 95mΩ | 3-LD, 4-LD, 7-LD, TOLL, PQFN88 | 4NCP(V)51752 30V Output Swing (SOIC-8) |
13NCD(V)5709x 32V Output Swing (SOIC-8) |
123NCD(V)5710x 32V Output Swing (SOIC-16WB) |
NCD(V)575xx 32V Output Swing (SOIC-16WB) |
1NCP(V)5156x 30V Output Swing (SOIC-16WB) |
| 750V | 13.5mΩ | 4-LD | |||||
| 900V | 16 – 60mΩ | 3-LD, 4-LD, 7-LD | |||||
| 1200V | 14 – 160mΩ | 3-LD, 4-LD, 7-LD | |||||
| 1700V | 28 - 960mΩ | 4-LD, 7-LD | |||||
Gate Driver: Peak Source Current / Peak Sink Current / Total Propagation Delay Matching
1 Supports: External Negative Bias Turn Off
2 Supports: Desaturation (Over current) Protection
3 Supports: Active Miller Clamp (Over current) Protection (clamps VGS preventing accidental turn on during intended turn off)
4 Supports: Internal Negative Bias Turn Off.
"V" Supports Automotive Qualification

| Short Description | |
| NCP51752 | 3.7 kV Isolated High Performance SiC Drivers |
| NCD5709x | 5 kV Isolated Single Channel Gate Driver |
| NCD5710x | 16-pin Wide Body Isolated Gate Driver |
| NCD575xx | 5 kV Isolated Dual Channel Gate Driver |
| NCP5156X | 5 kV Isolated High Speed Dual MOS/SiC Drivers |
| NCV51752 | 3.7 kV Isolated High Performance SiC Drivers |
| NCV5709x | 5 kV Isolated Single Channel Gate Driver |
| NCV5710x | 16-pin Wide Body Isolated Gate Driver |
| NCV575x | 5 kV Isolated Dual Channel Gate Driver |
| NCV5156x | 5 kV Isolated High Speed Dual MOS/SiC Drivers |
Specifications
Data Sheet
Reference Designs
Communication
Specifications
Data Sheet
Reference Designs
Power Management
| LDOs | |
| NCP189 | LDO, 500 mA, Low noise, High PSRR, Low V DO |
| NCP718 | LDO Regulator, 300 mA, Wide Vin, Ultra-Low Iq |
| NCP730 | LDO Regulator, 150 mA, 38 V, 1 uA IQ, with PGU |
| NCP731 | LDO Regulator, 150 mA, 38 V, 8 μVrms with Enable and external Soft Start. |
| NCP164 | LDO Regulator, 300 mA, Ultra-Low Noise, High PSRR with Power Good |
| Offline Regulators & Controllers | |
| FSL336LR | 650V Integrated Power Switch with Error Amp and no bias winding |
| NCP11184 | 800V Switcher, Enhanced Standby Mode 2.25 Ω |
| NCP1076 | 700V Integrated Power Switch, 4.8 Ω |
| NCP1251 | PWM Controller, Current Mode for Offline Power Suppliers |
| NCP1362 | Quasi-Resonant Flyback Controller with Valley Lock-out Switching |
| NCP1680 | Totem-Pole PFC Controller, CrM |
| NCP1568 | AC-DC Active Clamp Flyback PWM Controller |
| NCP13992 | Current Mode Resonant Controller |
| Protection Devices | |
| NUP2105 | 27 V ESD Protection Diode - Dual Line CAN Bus Protector |
| NUP3105L | 32 V Dual Line CAN Bus Protector in SOT-23 |
| ESDM2032 | 3.3 V Bidirectional ESD and Surge Protection Diode |
| ESD7551 | 3.3 V Bidirectional Micro−Packaged ESD Protection Diode |
| NCID9 series | High Speed Dual/3ch/Quad Digital Isolator |
| NIS3071 | TElectronic fuse (eFuse) 4-channel, 8 V to 60 V, 10 A in 5x6mm package |
| NCP3064 | Boost/Buck/Inverting Converter, Voltage Regulator, 1.5 A |
| NCS21 series | Current Sense Amplifier, 26 V, Low-/High-Side Voltage Out |
| NCS2007 series | Operational Amplifier, Wide Supply Range, 3MHz CMOS |
| LM393 | Comparator, Dual, Low Offset Voltage |
| NCS7041 | Current Sense Amplifier, 80V Common-Mode Voltage, Bidirectional |




