Robots are already one of the most popular applications at present. Whether in restaurants, factories or homes, robots have gradually replaced manpower and helped humans do some tedious and hard work. Looking forward to the future, with the maturity of artificial intelligence and robot technology, more robots will be involved in human society in the future and become the best helpers for human beings. This article will introduce you to the development of robots and the solutions that ADI can provide in robot applications.
Freeing humans from 3D automation work
Many people's definition of robots often stays in the humanoid robots in science fiction movies. In fact, robots already exist in our lives in various forms. Take a closer look around. Robots are already ubiquitous. Robots help deliver goods, deliver food, clean and answer guests' questions in grocery stores and restaurants. Some cobots (or called collaborative robots) work alongside humans helping with repetitive tasks in smarter factory floors. There are also some robots that enter our homes, helping with lawn trimming, vacuuming, and floor cleaning. Some robots are even providing lifesaving skills in hospitals sanitizing rooms and helping nurses lift heavy patients, saving caregivers from injury. Robots are redefining how we work, play and interact with each other, and their presence will undoubtedly play an integral part of our lives forever.
Today, manufacturers need to do more with less, handing over many dull, dirty and dangerous 3D automation tasks to robots. This relieves employees of tedious, repetitive tasks. Automation is driving the decline of banal and repetitive tasks, freeing up humans for more skilled and cognitive rewarding tasks, while also reducing injury risk. This worker enhancement maximizes employee potential, increases job satisfaction, and minimizes worker turnover.

Robots help solve industrial automation application needs
In industrial applications, robots have been widely used to perform some repetitive and heavy tasks, and have had a significant impact on the entire manufacturing industry. The industries are currently changing to keep up with consumer demand and behavior. Expectations for more customization and faster turn-around times on product production have forced manufacturers to change their operations to respond to this new demand, including more localized facilities with quickly reconfigurable production lines.
Industrial robots are facing new development trends, including the changing pattern of the manufacturing industry, ROI for automation is increasing, and the development of traditional robots in a more advanced direction. Robots that used to operate alone have also changed to work with humans. In addition, automatic guided vehicles (AGVs) and industrial mobile robots are also being rapidly popularized and applied. Advances in technology have greatly increased the possibility of robot adoption.
Industrial robots are facing many challenges. Through the improvement of collaboration, the limitations of automation have been gradually reduced, and human safety has been improved through more sensors. In terms of digital development, including Industry 4.0, machine health status, machine learning, Internet of things (IoTs) and big data, robots become easier to use, more flexible, and support plug-and-play interfaces through simplified processes.
Increasing consumer demand is driving a shift away from low mix, high volume manufacturing towards high mix, low volume manufacturing, which demands greater flexibility on the factory floor. For example, consumers may need a sports car with special letters, patterns and colors engraved on the hood, or require more customized configurations on the interior. Due to the popularity of robots, this small and diverse customization is achieved. Beyond this, ROI for automation is increasing as robots become more affordable while enabling greater productivity and flexibility.
The rapid rise of collaborative robots that work alongside humans
Traditional industrial robots like those seen at auto manufacturers, operate at high speed and often with very large payloads, so they need to be separated from humans using safety cages or light curtains. These types of robots must continue to advance to solve problems such as multi-axis synchronization, high-precision motion control, optimized size to solve space constraints, more efficient power conversion, functional safety, reliability and uptime and other challenges.
Collaborative robots (cobots) are also on the rise and are enabling automation of tasks that were previously only possible with humans. Cobots are much easier and cheaper to install than traditional industrial robots and have a lower purchase cost. Businesses can install and set up the robot and program it themselves. This leads to more manufacturers adopting automation where they previously could not afford to, all the while experiencing a reduced total cost of ownership (TCO). Cobots have addressed challenges in functional safety, proximity sensing, cabling, mid-range motion control, more efficient power conversion, orientation sensing, and more.
The current revolution brought about by robots is quite diverse, such as assisting in the pivoting manufacturing lines flexible automation allows seamless tool changes, plug-and-play interfaces and fast reprogramming so robots can redeploy from an existing task, such as dressmaking, and pivot to something new like making healthcare masks or gowns., in which cobots will play an important role.

Global pandemic drives robot adoption rapidly
The application of robots and automation is not limited to the manufacturing industry. Under the global epidemic, workers in manufacturing, logistics, and workplaces need to keep a distance. Hospitals, airports and other places often need to be cleaned and disinfected. The movement of objects, picking and packing of goods in distribution centers, and other tasks have accelerated the adoption rate of robots.
Robots can assist employees to maintain social distance or isolation. In times of crisis (or epidemics), manufacturing, logistics or recycling centers are where robots can play their role. Placing robots between employees can not only achieve the necessary isolation, but also supplement the missing workforce, thereby maintaining productivity.
In addition, cleaning and disinfection in hospitals, airports, malls and public spaces are where robots really earn their keep. AGVs are faster, more effective than manual cleaning by humans, as they use UV light to disinfect hospital rooms, compared to spraying. Robots in medical facilities will assist with material transportation and handling, be able to navigate completely on their own, even ride in elevators without human intervention. They can dispense medicines or move samples to laboratories, thereby increasing efficiencies and decreasing human exposure to dangerous materials. At present, AGVs have solved the challenges of navigation, stability, high-efficiency power conversion, battery management, wireless communication, and functional safety, and they are being widely adopted in various industries, hospitals, warehouses, and other fields.
There is no doubt that online shopping will continue to grow on a large scale in the future. In the past, distribution centers used manual picking and packaging, which is very labor-intensive. This means that the unique capabilities of robots will be the best solution for distribution centers. Partners can use robots to quickly and accurately complete the picking and packaging of orders, achieving next-day (or same-day) delivery services and improving consumer satisfaction. The use of robots will be an essential development direction for distribution centers.
Conclusion
While pessimists will continue to follow the sky-is-falling-prognostications about robots eliminating humans and the potential negative outcomes of automation causing unemployment, maintaining a calm and thoughtful approach and actively embracing positive change for the future will lead to a completely different way of thinking. The very real contribution of automation and robotics to human productivity, safety, competitiveness and job creation is enormous. In these ever-changing pandemic times, robots will play a key and expansive role in supporting society and helping with the recovery, while reducing dependency on global supply chains and reshoring manufacturing. And that’s something everyone can look forward to experiencing.
For those afraid of robots replacing human jobs, the technology used in many jobs where robots are used is simply unable to match the complexity of the human brain. Tasks requiring human skills, such as empathy, critical decision-making, or procedural knowledge, cannot be replaced by robots. Humans can be freed from dull, dirty, and dangerous work to perform tasks that are more valuable and interesting and reduce the risk of injury.
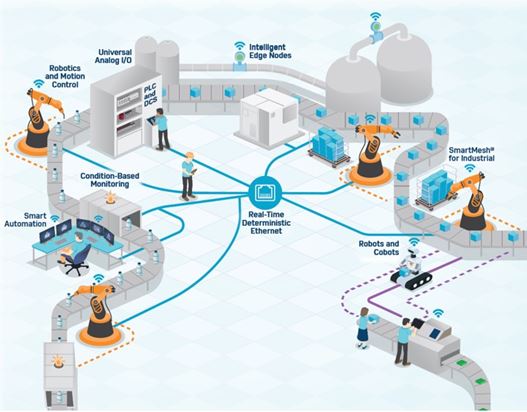
ADI has been committed to developing the relevant technology required for robot applications, including industrial Ethernet solutions, SmartMesh® wireless networks, power products by Linear, machine health monitoring, battery management, stabilization and orientation technology, navigation and mapping, proximity detection, cyber security, functional safety, servo drive signal chains, among other technologies. ADI focuses more on the system level rather than just components, combining software solutions with the development of artificial intelligence and algorithms to provide customers with a more comprehensive and complete solution and technical support.

